Key Areas
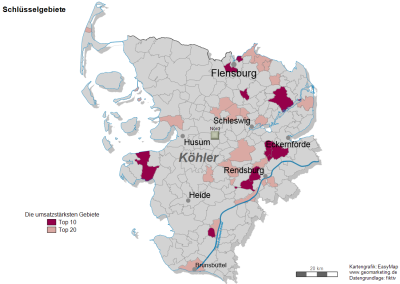
With the analysis key areas in the menu area organisation Identify the most valuable or significant areas within of any territory.
For this purpose, easymap creates a new design for the bricks of each territory of so-called quantiles, related to the selected column. This means, easymap sorts the areas within the territories in descending order by of the selected column, cumulates the data values and forms classes for the cumulated values. All areas that fall into the same class, will then have the same surface colour in the map.
This not only allows you to see which areas have the largest but also how they are distributed throughout the surface.
Note: In addition to the global evaluation across all areas of the structure and the percentage, district-related evaluation, you can use the district-related evaluation (ranking) option to highlight the bricks with the highest turnover in your territory structure in color. This option puts the values of a column in descending order and colors the first x areas according to the class formation.
For example, in order to color the ten bricks with the highest turnover per area, the data column with turnover figures should be selected, the number of classes should be two and the class boundary should be ten. Of course, you can also set a higher number of classes with a descending color intensity to highlight possible high-turnover area agglomerations.
Creating the Analysis Key Areas
You can access the analysis via the menu Territory organization > Analyses > Key areas. First, you are asked at which level of the territory structure key areas are to be calculated.
Alternatively, you can also insert the key areas in the control window Territory organization in the context menu of the area level under Analyses.
Select data input and connect the data to the map
For your analysis, select the appropriate assignment between data and levels and confirm your selection.
- What does the assignment result tell you?
- Would you like to place your data on the map using geographical coordinates? So the The Data Input for an Analysis.
- The Advanced button allows you to specify whether the analysis should consider an existing clip map when calculating classifications - more on the analysis reference.
Edit Properties
Immediately after inserting the analysis, the Properties on the right side of the program window open (default setting). The properties can be reopened at any time via the control window Content by double-clicking on the map layer Key areas.
Determine the coloration of key areas
In this analysis, similar to the analysis surface coloring, the column to be analyzed can be selected. The default setting here is area. Under Statistics you will find various indices for the selected column. The areas of the brick level of the selected level can be colored here classified, by the formation of classes.
Comparability of territories
Choose here between:
| Global evaluation (absolute) | Sorts the bricks of all territories in descending order by of the selected column, cumulates the data values and creates classes. for the cumulated values. |
| Territory-based Evaluation (by Percentage) | Sorts the bricks of a territory in descending order by of the selected column, cumulates the data values and creates classes. for the cumulated values. |
| District-Related Evaluation (Ranking) | Sorts the bricks of a territory in descending order according to the selected column and colors the first x areas, depending on the structure of the classes. |
Classes Education
The creation of classes offers you numerous setting options. In addition to the number of classes or move-in areas, you can also define how the limit values of the classes are to be determined.
In the middle area, enter Classes, the Count for classes, and the method of automatic Classification or set here to User defined to edit your own classes. In addition to Analysis range, you can also specify an interval within which the values are to be taken into account. Values outside the interval always fall into the residual class "unclassified".
- In the lower area you can then determine the details (class list) of the analysis. Various commands are available here to edit classes and colors.
- The design characteristics and class boundaries can be edited by double-clicking in the relevant cell. For example, you can select the color individually by double-clicking on the color of the class.
- For more information on editing classes, symbols, colors and sizes, see here.
Note: By sorting according to the name of the class, you can force a certain order in the legend!
Determine the details of the analysis
In Details you define other (non-data-dependent) properties of the analysis.
| Visibility | |
| General |
Here you can control the visibility of objects and elements. |
| Scale range |
Here you can set whether the selected object or plane should be visible at each scale. Or you can specify the scale or zoom level at which the object or layer is visible. |
| In reports |
In Reports there is the possibility to change the environment only partially to zeigen. You can use this property to specify whether the layer is also visible outside the report area in this case. |
| Alternating visibility group |
Set a group for mutual visibility here. If the element is to be made equally visible with other elements, you must use the same name for the visibility group. |
| Simultaneous visibility group |
Set a group for simultaneous visibility here. If the element is to be made mutually visible with other elements, you must use the same name for the visibility group. |
| Calculation | |
| Missing data |
Don't calculate the result value: Only for bricks for which data is available is a result value of the analysis calculated. This selection can lead to results where only individual areas are colored. Treat as 0: Bricks for which there is no value are also included in the analysis. Their value is treated as 0. As a result, such areas may well get a value greater than 0. This selection leads to area-wide coloured maps. |
| Use geographic barriers |
Specify whether EasyMap calculates the distance of a brick to the territory location using the linear distance or whether it additionally includes topographic obstacles (barriers) such as mountains, rivers or bays in the distance calculation. These are read from Barrier-base map |
| Common | |
| Type of Shading | Here you can select whether the color of the areas full area or only as edge color should appear. With this option, loosened maps are possible, which allow not only the analysis of the surface coloration but also a further evaluation, without the map appearing overloaded and not really readable. |
| Width of the Colored Border |
Here you can set the width for the edge coloring in cm . |
| Comment | Enter here a comment for the display of the workbook in EasyMap Xplorer. The comment is also displayed in EasyMap as a tooltip in the control window Contents. |
| Hatching - Display of the distance zones with multiple assignment. | |
| Type |
Here you can choose the type of hatching. |
| Width |
Set here the hatch width in pixels. |
Create tooltips for analysis
When crossing the colored areas on the map, you can display context-sensitive information about them.
Note: You can find out how to implement tooltips here.
The commands of the context menu
You can right-click on the analysis in the control window Content to open its context menu. The context menu provides actions that can be performed on this analysis.
| Transfer Selection to |
Transfers the current selection geographically to another object. Details... |
| Visible |
Shows whether the object is visible and allows switching the visibility. |
| Order |
Here you can change the selected element in the character sequence. Another option is to drag and drop the selected element within the content view. |
| Input Data... |
Displays the data settings for the selected analysis. You can use this command later to change the connection between the analysis and the data. Further information can be found here. |
| Show Results Table | Displays the results of the selected analysis in a table. |
| Ignore filter |
Defines whether an Analysis filter should be considered or not. |
| Restore defaults |
Undoes all manual changes to this layer. |
| Clip Map |
Here you can define a different clip map for the analysis. |
| Map XY |
Here you will find various commands for the map. |
| Copy |
Copy the object (if necessary with all subobjects) to the clipboard to paste it elsewhere. The object can be inserted in other applications as a graphic, or inserted in EasyMap as a copy of this object using the Insert command. |
| Paste |
Pastes the contents of the clipboard into this object as a child object. |
| Delete | Deletes the selected element. (See also: delete objects) |
|
Rename |
Changes the content view to an edit mode to give the object a new name. (This can also be achieved by clicking on an object that has already been marked.) |
| Properties... |
Opens a properties dialog in which you can edit the Properties of the selected object. If several objects are selected, many properties can also be changed simultaneously for these objects. |