Report on filters
In the filter report, analyses are modified by varying a filter on the data. For example, you can automatically split a complete map showing all A, B and C customers and display only A customers on one report page, only B customers on the next and only C customers on the third report page.
Affected analyses
A filter report influences the display of all analyses that use the table on which the report is based as the data basis. The only exceptions are the analyses with the Ignore filter setting.
Filter definition
First select the table that contains the data to be filtered. Then select one of the two filter types Auto-Filter or User defined. Both options allow you to include a unfiltered view. This means that an additional view is created without the filter set.
Filter type Auto-Filter
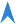
With the filter definition shown on the right, a filter report is generated which applies various filter settings to the column "Classification" in the table "Customer master". The selected Auto-Filter of type characteristic results in the creation of one report page each, in which only the data records with the value A-Customer or B-Customer or C-Customer in the data column "Classification" are considered and displayed in the analyses. In total, this report thus provides three pages.
Filter type User-defined filter
If the possibilities of the Auto-Filter filter type are not sufficient for you, you can use the user-defined filter. Here you can create your own filter definitions. Use the Plus button to add a new filter definition. Either enter the filter expression in the field under Filter definition directly with the keyboard or use the button next to the column Name to get to a filter editor with different expression categories.
Output Details - Uniform Classes
If you select the option Uniform classes=Yes under Output details, easymap considers all data (and not only filtered data) for each individual map when calculating the classes used in analyses. If Uniform classes=No is selected, easymap considers only the filtered data for each individual map when calculating the classes used in analyses.
Note: The option Uniform classes is only relevant for automatic classifications (e.g. Equally distributed). For user-defined classes it is of no importance.