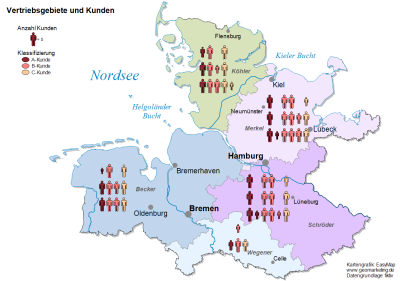
Unit Charts
The analysis Unit Charts generates symbol groups in which the number of symbols is determined by the respective data value. The diagrams then consist of several stacked symbols.
Creating a New Analysis
Insert the Analysis Unit Charts via the menu option Analyze. Inserting a new analysis is done in three steps.
1. Analysis Type
In the first step, select an Analysis Subtype. You can choose between a site-related and a area-related representation of the diagrams. The analysis type determines whether a diagram is generated per area (area-related) or per data set (location-related).
2. Select data input and connect the data to the map
After selecting the analysis type, continue with the selection of the data basis.
- First select the Table that contains the data to be displayed in the analysis.
- In addition, you specify on which sheet and in which map the analysis is to be displayed.
- Then check whether the column with the area number (e.g. postal code) from the table corresponds to the corresponding level (e.g. postal code areas - areas) of the base map. The area number is used to assign the individual data records to the corresponding area.
- What does assignment result?
- Would you like to place your data on the map using geographical coordinates? So the Place data using geographic coordinates.
- Via the Advanced button you can specify whether the analysis should consider an existing clip maps in the calculation of classifications - more about Analysis reference.
3. Set Properties of the Analysis
Properties refers to all settings for calculating and displaying the analysis. You can select certain columns of the previously defined table to control certain aspects of the display (for example, the color). You also reach this settings dialog if you want to edit existing analyses.
The most important settings beside the selection of the data columns to be evaluated are in the Details section. Under Style you first select the symbol to be displayed in groups. By default, the circle is selected here. With Value per Symbol you can enter which data value a symbol should correspond to.
Chart
Under Diagram you define which data the diagram should display. You can also specify the coloring and size proportions of the diagram and other diagram options.
In the Chart section, select the count of columns to be evaluated. Only number columns are used for the evaluation. In the list, the columns appear as they are listed in the table. Now select the column to be evaluated for each column or bar in the Data column. The name of the column for the legend appears under caption (but it can also be changed accordingly). The maximum number of possible symbol groups corresponds to the number of number columns in the selected table.
The colors of the individual symbol groups can be selected by clicking on the button ColorsLoad, Save or Color gradient. In addition, each color can be controlled individually by double-clicking on the respective color field. Each symbol group can also have certain properties of the filling, such as hatching or gradient.
Via the Load button under Colors you can access a series of color palettes prefabricated in EasyMap or you can navigate to a color palette (.pal file) individually compiled by you. The color palette file is created via the Save button.
As already mentioned, it is easiest to assign the Value per Symbol in the Details section. The following options are available for determining the chart size:
| Size Proportion | |
| Smallest, average and largest chart |
You can specify the size of the displayed symbols here. You use the three properties to define a common proportionality factor that specifies the conversion between the data value and the diagram size. Therefore, changing one of the three values automatically leads to the adjustment of the other values. Due to the underlying data and proportionality, there is a complicated relationship between the three reported values. |
| Specific Chart |
Enter the value or the size for a diagram. An entry in the Size area also automatically changes the values for the smallest/medium/largest diagram. An entry in the range Value leads to a corresponding conversion for the size of the diagram, but not for the specifications of the smallest/medium/largest diagram. |
| Data Update | |
| Dynamic sizing |
Here you can set how the diagrams should behave when data is changed. Preserve ratio: The conversion factor between the incoming values and the size of the diagram is retained even after data changes. If, for example, considerably larger values are obtained after a data change, you will also receive larger diagrams. Get maximum diagram size: The maximum diagram size you specify is also guaranteed after data changes. However, this means that the diagrams are scaled differently, i.e. the conversion factor between the input values and the diagram size must be adjusted. |
|
Note: If you want to use a chart analysis to display highly variable data and prevent charts from growing too large, use the second option. If the comparability of the diagrams is in the foreground, use the first option. |
|
| Threshold Value | Here you can determine a threshold or a threshold that a diagram must have at least to be displayed. |
| Statistics |
Here you can find the statistical values for the total diagram. They can be used to help determine suitable diagram sizes. Average Sum: For each row, calculates the row total for the selected columns and returns the average of all rows. (Average total = total sum / number of table rows). Total: Displays the sum of all selected columns and rows. |
Determine the details of the analysis
In Details you define other (non-data-dependent) properties of the analysis.
For example, you may set the sorting of the groups of symbols in the Details section, or define the Symbol and Value per Symbol.
| Visibility | |
| General |
Here you can control the visibility of objects and elements. |
| Scale range |
Here you can set whether the selected object or plane should be visible at each scale. Or you can specify the scale or zoom level at which the object or layer is visible. |
| In reports |
In Reports there is the possibility to change the environment only partially to zeigen. You can use this property to specify whether the layer is also visible outside the report area in this case. |
| Size adjustment |
Specify here how the size of a symbol or diagram behaves when the map scale is changed. This can change e.g. after zoom within the map, after setting a clip map or within a report, because only a part of the map is displayed. More about Size adjustment at auto zoom. |
| Alternating visibility group |
Set a group for mutual visibility here. If the element is to be made equally visible with other elements, you must use the same name for the visibility group. |
| Simultaneous visibility group |
Set a group for simultaneous visibility here. If the element is to be made mutually visible with other elements, you must use the same name for the visibility group. |
| Style | |
| Sort table |
Allows you to sort the circle segments or bars according to the size of the class. You can sort the bars or sectors either Descending or Ascending. The Appropriate Definition option sorts the bars/segments in the order in which they were selected when the analysis was created (see Order in the Diagram tab). |
| Symbol | Defines the graphic display of the unit chart. Clicking ... you can choose from a wide range of preset icons in EasyMap or select your own icon in .emf format. |
| Display Partial Symbols |
If a value is displayed in the form of a number of symbols, there is usually a remainder that is smaller than the value per symbol. The remainder can either be displayed as a proportionally reduced symbol or as a proportionally truncated graphic. Example: A municipality has 105 inhabitants. The user has chosen 10 as Value per Symbol, i. e. one symbol represents 10 inhabitants. A unit chart with 10 symbols thus represents 100 inhabitants. To represent 105 inhabitants, EasyMap adds half a symbol if you select the option Cut. However, if you select the option Collapse, EasyMap adds a semi-sized icon. |
| Value per Symbol | Determines the data value for one symbol. |
| Show original location | |
| Here you can determine what happens when a diagram is moved. Here a line can indicate the original position and thus an easier allocation of the data and orientation can be achieved. To display the original position for all diagrams, select all diagrams in the map and open the Properties of the several selected objects from the context menu. In the Display item, you can specify that the original position should be displayed (select Yes setting). | |
| Style, Line Width, Line Color, Start, End | Here you can set how the arrows between text and position point are to be displayed. You can specify the start and end points of the lines, the line width/color, and the style. Applications and other settings for the original position indicator can be found here. |
| Arrangement | |
| Max. Number of Columns on Display | Enter the maximum number of columns to be displayed. |
| Separate by Data Columns | If you want to divide the symbol groups according to the data columns, enter Yes here. Setting No, the columns are filled with the symbols. |
| Fill up Columns |
The selection Ascending fills the columns with icons from the bottom up. Descending fills the columns from the top to the bottom. |
| Symbols per Column | Specify the number of symbols per column. Please make sure that the combination with Max. Number of Columns and Value per Symbol matches, so that all symbols can be displayed. |
| Data Labeling | |
| Format |
With Formatting of the numbers you can specify whether large numbers with thousands separators are displayed more legibly, or small numbers with many or few decimal places are drawn. |
| Content |
You can label the diagrams with value, percent or name. All labeling elements can also be displayed simultaneously. If you deselect all check marks for the content, no label will be inserted and all properties in the Data Labeling section have no meaning. |
| Angle |
For the labeling you can define an angle. This allows you to make long rows of numbers legible in an inclined position - if they were side by side, they would overlap. You can choose between 0° (horizontal), 45° (oblique). 90° (vertical). |
| Font, Font Color |
Set here the font and size as well as the font color. |
| Common | |
| Comment | Enter here a comment for the display of the workbook in EasyMap Xplorer. The comment is also displayed in EasyMap as a tooltip in the control window Contents. |
| Shadow | |
| 3-D Shadow |
In addition to the shadow display, you can also select 3D shading to make the objects appear three-dimensional. This variant may not be supported by all printers. |
| Shadow Color |
Specifies the color in which a shadow representation of the object is to be drawn. You can specify the color using the color selection field or directly as HTML color value. If no color is specified, no shadow is displayed. |
| Shadow Spacing |
If a shadow is displayed to the object, the distance or width of this shadow can be set here. |
Labeling
In addition to labeling the groups of symbols, each chart may cotnain a label that applies to the entire chart (for example, the name of the area to which the chart refers). The settings for this can be defined under Labeling.
- If the analysis area-related is created, EasyMap offers the possibility to label each symbol or object with the name or number of the corresponding area (geographical data).
- With the analysis subtype Location-related, however, only the columns of the data table used as the data basis for the analysis can be used for labeling.
Note: How to insert diagram texts and how to influence the display of the texts can be found here.
Tooltip
When driving over the diagrams on the map, you can display user-defined information about them.
Note: You can find out how to implement tooltips here.